Whether mild or severe, receding gums pose a concerning threat to your oral health. As gums recede, they unveil tooth roots and edges that should ideally remain protected. This prolonged exposure can open the door to a range of serious oral problems like infection, decay, and, of course, periodontitis. Our dedicated team of gum treatment experts provides specialized treatment options to ensure optimal gum care, but you first need to know how to identify and prevent the signs of receding gums in the first place.
How to Prevent Receding Gums: Treatments and Proactive Factors
For those unfamiliar with the nuances of gum health and the risks of recession, discovering the impact of a receding gum line can be alarming. Therefore, to empower you with the knowledge to safeguard your gums, our amiable staff has crafted this concise guide, enabling you to take swift control of your oral health. Keep reading to learn more about how to prevent receding gums: treatments and proactive factors.
What is Gum Recession?
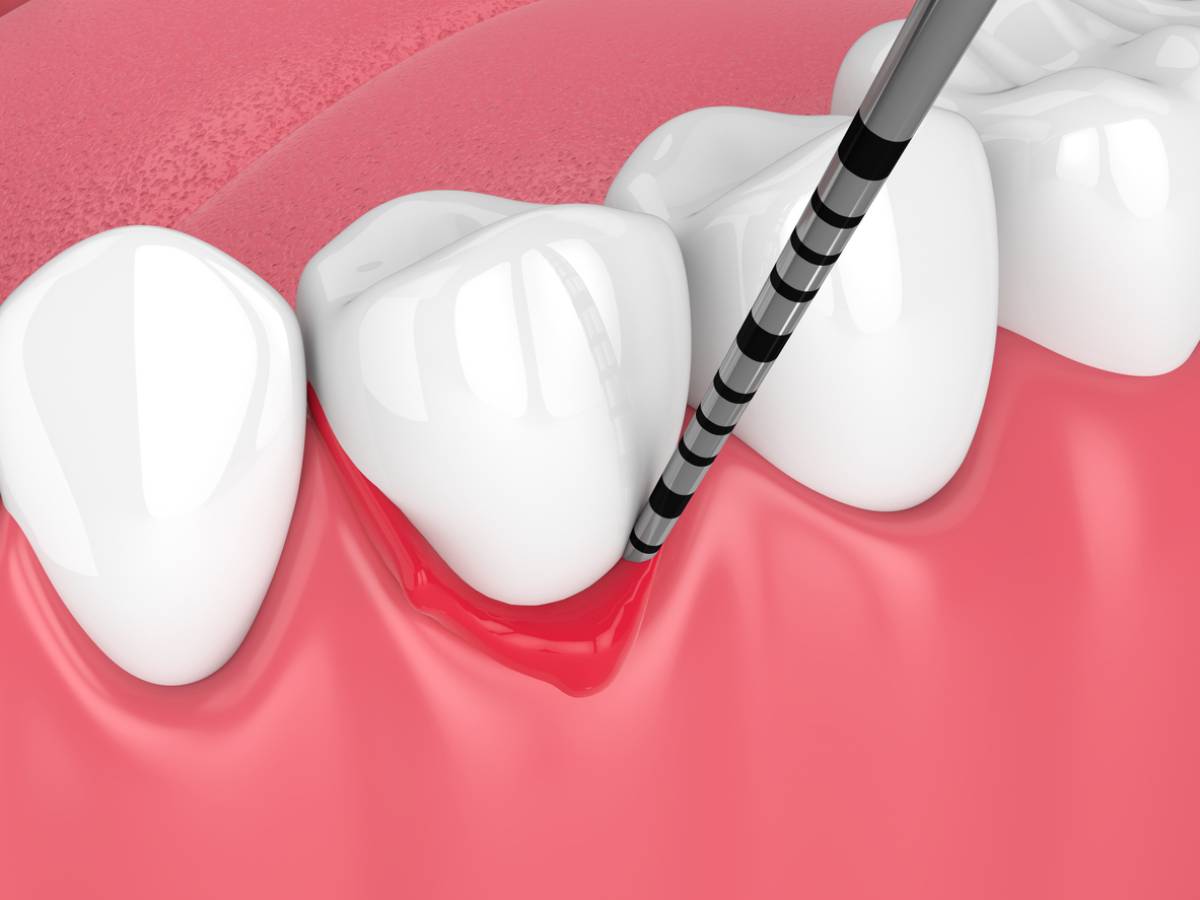
Gum recession is defined as an infection that starts in the tissue above the teeth, which typically serves as a barrier between the teeth and the gums. Multiple factors can contribute to the initiation of gum recession, leading to the formation of gaps between teeth and gum over time.
These gaps create a perilous opening for bacteria, disease, decay, and infection to infiltrate, fostering the growth of harmful microbes and escalating dental complications. If left untreated, receding gums can culminate in tooth loss, compromised bone structures, gum disease, and even more deadly oral concerns.
What Causes Gum Recession?
A myriad of signs and symptoms can point to gum recession, each warranting prompt consultation with your trusted dentist. Some of the most common causes of gum recession may include:
- Aggressive Brushing: Overzealous brushing can erode tooth enamel, setting the stage for gum recession.
- Periodontal Disease: This is the most advanced stage of gum disease, meaning that your gums have already started to recede.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting dental care contributes to gum and tooth decay, making your need for dentist intervention more immediate.
- Genetics, Hormones, and Smoking: Genetic predisposition, hormonal fluctuations, and chronic smoking can exacerbate gum recession, especially when coupled with gum disease.
Consistent oral hygiene practices form the cornerstone of gum recession prevention. Still, regular brushing and flossing may seem routine, yet they wield significant long-term impact. Opt for a toothbrush with soft bristles to minimize gum irritation during brushing.
Prevent Gum Recession Now
Whether you’re concerned about emerging signs of gum recession or already experiencing symptoms, proactive oral care is paramount. While overall dental hygiene remains essential, particular attention to emerging symptoms is crucial. Don’t forget to reach out at the slightest sign that something is wrong.
Here are additional measures to avert enduring gum issues while you get in touch with your dental care experts:
- Quit smoking to reduce the risk of gum recession and associated complications.
- Monitor mouth changes and consult your dentist if any irregularities arise.
- Kick bad chewing habits to the curb, protecting your gums from unnecessary strain.
- Invest in optimal nutrition for healthy gums and teeth.
- Refrain from using teeth to open non-food items or objects.
If you detect the initial signs of gum recession, you can act quickly to prevent your oral health from getting worse. If left untreated, your symptoms of receding gums can make way to full-blown periodontitis – which is painful and hard to treat. Make sure to contact our dental office as soon as you can and we can help you schedule a personal consultation. Getting the right diagnosis early on is key to finding a treatment plan that works for you.